Global warming is a long-term rise in the average temperature of th...
<<GotoNote
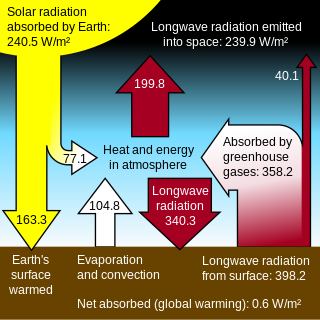
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without its atmosphere.[1][2]
If a planet's atmosphere contains radiatively active gases (i.e., greenhouse gases) they will radiate energy in all directions. Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, warming it.[3]
The intensity of the downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – will depend on the atmosphere's temperature and on the amount of greenhouse gases that the atmosphere contains.
Earth’s natural greenhouse effect is critical to supporting life. Human activities, mainly the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests, have strengthened the greenhouse effect and caused global warming.[4]
The term "greenhouse effect" is a misnomer that arose from a faulty analogy with the effect of sunlight passing through glass and warming a greenhouse. The way a greenhouse retains heat is fundamentally different, as a greenhouse works mostly by reducing airflow so that warm air is kept inside.[2][5][6]
...https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greenhouse_effect